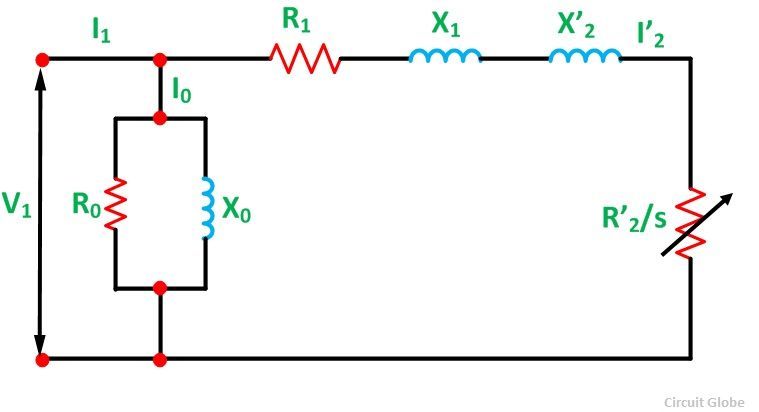
How to Draw Circle Diagram of Induction Motor in Matlab
The Circle Diagram of an Induction motor is very useful to study its performance under all operating conditions. The structure of the circumvolve diagram is based on the guess equivalent circuit shown beneath. Information technology is the diagrammatic representation of the performance of the induction motor. The circle diagram provides data nigh the ability output, losses, and the efficiency of the induction motor.
Contents:
- Construction of the Circle Diagram
- Result Obtained from the Circle Diagram
- Significance of lines on the Circumvolve Diagram
Applying KCL (Kirchhoff's Current Law)![]()
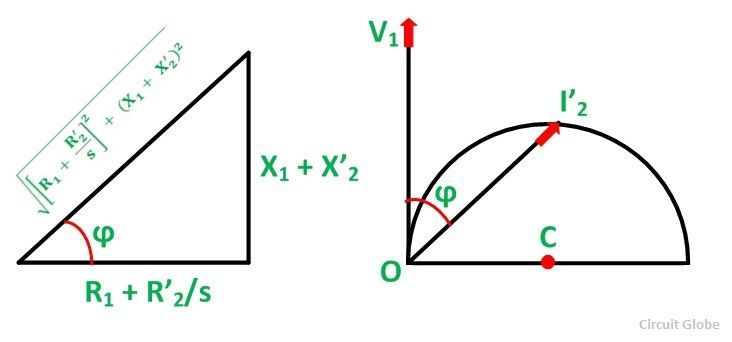
Let the phase voltage 5i exist taken along the vertical centrality OY as shown in the figure beneath:
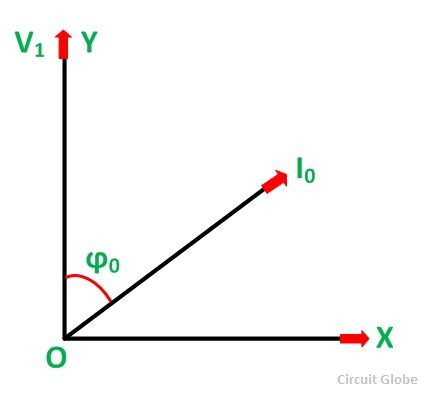
The No-Load current I0 = OA lags behind 51 by an angle ϕ0. The no-load ability gene bending ϕ0 is of the club of 60 to 80 degrees considering of the big magnetizing current needed to produce the required flux pole in a magnetic circuit containing the air gaps.
At the no-load condition, due south = 0 and R2/south are infinite, or we tin say that the R2/s is an open up circuit at no load.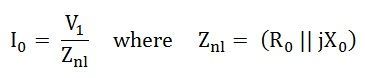
Here, all the rotational losses are considered nether R0 and the no-load loss is given by the equation shown below:![]()
The rotor current referred to the stator is given by: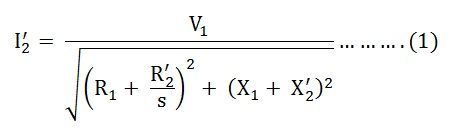
The current I'2 lags behind the voltage V1 past the impedance bending ϕ every bit shown in the effigy below:
Where,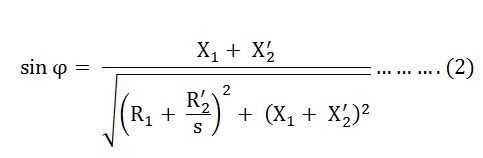
Combining equation (1) and (2) we get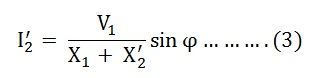
The above equation (3) is of the form r = a sin φ which represents a circumvolve in polar course with the bore a.
From the in a higher place figure (b) shown, the following points are illustrated.
- The locus of I'two is a circle of the diameter V1/ X1 + X'2
- The radius of the circumvolve O'C = Five1/ 2(Xone + X'2)
- The centre C has the coordinates [V1/ two(101 + 10'2), 0]
The resulting circle diagram of the induction motor is shown below:
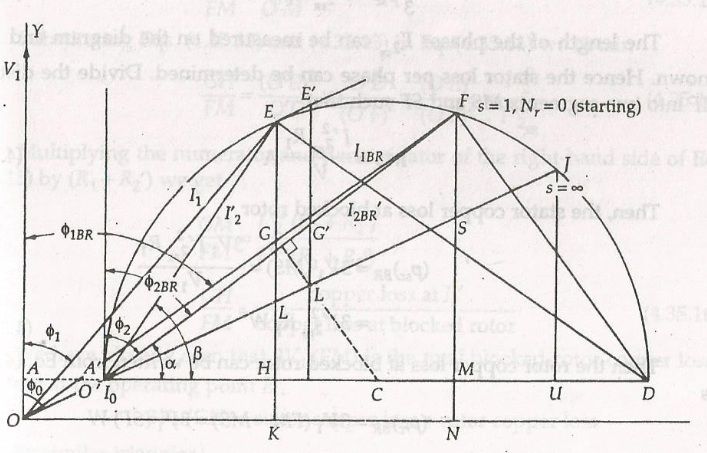
It is seen that the tip of the phasor I1 coincides with that of the phasor I'2. Thus, the locus of both Iane and I'2 is the upper semicircle. I1 and I'2 radiate from the origin O and O' respectively. When the motor is started s = one with the rated voltage, the tip of I1 and I'two will be at some point F of the circumvolve.
As the motor accelerates, the tips of Ii and I'2 move effectually the circle in an anti-clockwise direction. This process continues until the output torque matches the load torque. If there is no shaft load, the motor accelerates to synchronous speed. At this betoken I'2 = 0 and I1 = 0.
Construction of the Circumvolve Diagram
The following data are required for amalgam the circle diagram:
- Stator stage voltage Five1 = VL/√3
- No-load current I0
- No-load power cistron cosϕ0
- Blocked rotor current and power factor
- Stator phase resistance R1.
Steps to describe Circle Diagram of an Induction Motor:
- Take the phasor voltage Vi along the y-axis.
- Choose a user-friendly current. With O every bit origin, draw a line OO' = I0 at an angle ϕ0 with Vone.
- Draw the line OKN perpendicular to Fiveone. Similarly, depict a line O'D perpendicular to Vi.
- From signal O depict the line equal to the blocked rotor current I1BR to the same scale as I0. This line lags behind Vi by the blocked rotor power factor angle ϕ1BR.
- Bring together O'F and measure its magnitude in amperes. The line O'F represents I'2BR.
- From point F, draw a line FMN parallel to 5i. This line is perpendicular to O'D and ON.
- Calculate MS = I'2 2BRR1/Vane and locate signal S. Bring together O'S and extends it to meet the circle at J.
- Describe the perpendicular bisector of the chord O'F. This bisector will pass through the middle of the circle at betoken C. Now with the radius CD' or CD draw the circle.
Issue Obtained from the Circle Diagram
Assume that the line current Iane is known. With the centre at O, draw an arc with the radius Iane. This arc intersects the circle at the operating betoken E. Draw the line EK and locates the betoken H, L, G.
The following results are obtained from the circumvolve diagram shown above.
- Input ability = 3V1 KE
- Rotational losses = 3V1 KH
- Stator copper loss = 3Vane HL
- Rotor copper loss = 3V1 LG
- Output power = 3Vi GE
- Output torque = 3V1 LE/ωdue south
- Starting torque = 3Vane SF/ωs
- Slip = LG/LE
- Speed = GE/LE Ten ns
- Efficiency = GE/KE
- Power gene = KE/OE
Significance of lines on the Circle Diagram
Input line ON
The vertical distance between any point on the circle and the line ON represents the input power. Therefore, line ON is called the input line.
Output Line O'F
The vertical distance between any betoken on the circumvolve and the line O'G represents the output power. Hence, line O'F is called the output line.
Air Gap Power Line O'J
Line EL represents the air gap power Pg; line O'L is referred to as the air gap power line. Since, Ʈd = Pg/ ωs. This line is also known as Torque line.
Source: https://circuitglobe.com/circle-diagram-of-an-induction-motor.html
0 Response to "How to Draw Circle Diagram of Induction Motor in Matlab"
Post a Comment